Standard Consistency and Initial Setting Time of Cement
INTRODUCTION
Standard Consistency of Cement :
The Standard Consistency or Normal Consistency of a cement paste is defined as that consistency or percentage of water to be present in the cement paste which will permit a Vicat plunger having 10mm diameter and 50 mm length to penetrate to a depth of 33-35 mm from the top of the mould. Standard consistency test is conducted to find out the amount of water to be added to the cement to get a paste of normal consistency i.e., paste of certain standard solidity. This is used to fix the quantity of water to be mixed in the cement before performing tests for setting time, soundness and compressive strength. The standard consistency is the consistency which will permit the Vicat plunger having 10mm diameter and 50mm length to penetrate into a depth of 33-35mm from the top of the mould. The particular amount of water which allows the plunger to penetrate only to a depth of 33-35mm from the top is known as the percentage water required to produce standard consistency. The percentage is usually denoted as P. The test is required to be conducted at the standard temperature of 27±2°C and constant humidity of 90%.
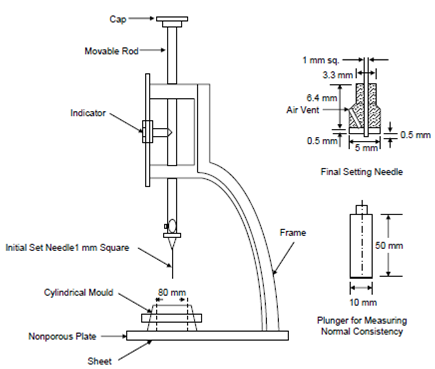
Specification of Vicat Apparatus used for Consistency Test
( Source : http://civilblog.org/2014/08/01/how-to-determination-of-standard-consistency-of-cement-paste/ )
For setting time test, the water quantity=0.85P; where P=amount of water required for standard consistency. Water quantity required for soundness test=0.78P and for compression strength test is "(P/4+0.3)" combined mass of cement and sand.
Initial Setting Time of Cement :
Setting time of cement paste, mortar or concrete will have a influence on handling of cement or concrete. The setting time is divided into two parts, i.e., initial setting time and final setting time. Initial setting time is the time elapsed between the moments that the water is added to the cement, to the time that the paste starts losing its plasticity. The final setting time is the time elapsed between the moment water is added to the cement and the time when the paste has completely lost its plasticity and has attained sufficient firmness to resist certain definite pressure.
It is important to know the setting time of cement paste, mortar or concrete in a actual constructions because the process of mixing, transporting, placing, compacting, finishing requires certain time. During this time the cement paste, mortar or concrete should be in plastic condition. The time interval for which the cement products remain in plastic condition is known as the initial setting time. Normally a minimum of 30 minutes is given for mixing and handling operations. The constituents and fineness of cement is maintained in such a way that the concrete remains in plastic condition for certain minimum time. Once the concrete is placed in the final position, compacted and finished, then it should lose its plasticity in the earliest possible time so that it is least vulnerable to damages from external agencies. Gauging time is the time elapsing from the time of adding water to the dry cement until commencing to fill the mould.
Setting time for different types of cements :
| Type / Name of cement | Referenced Indian Standard | Initial Setting Time, minutes (min) | Final Setting Time, minutes (max) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OPC(33) | IS:269 | 30 | 600 |
| OPC(43) | IS:8112 | 30 | 600 |
| OPC(53) | IS:12269 | 30 | 600 |
| PPC | IS:1489, P1 | 30 | 600 |
| SRC | IS:12330 | 30 | 600 |
| PSC | IS:455 | 30 | 600 |
| High alumina | IS:6452 | 30 | 600 |
| RHPC | IS:8041 | 30 | 600 |
| Low heat | IS:12600 | 30 | 600 |
( Source : http://civilblog.org/2013/05/04/initial-final-setting-time-is-4031-part-5-1988/ )
Relevant Indian Standard for Tests on Cement :
IS 4031 (Part-5) -1988: Methods of physical tests for hydraulic cement, Part 5: Determination of Initial and Final Setting Times, First Revision.
